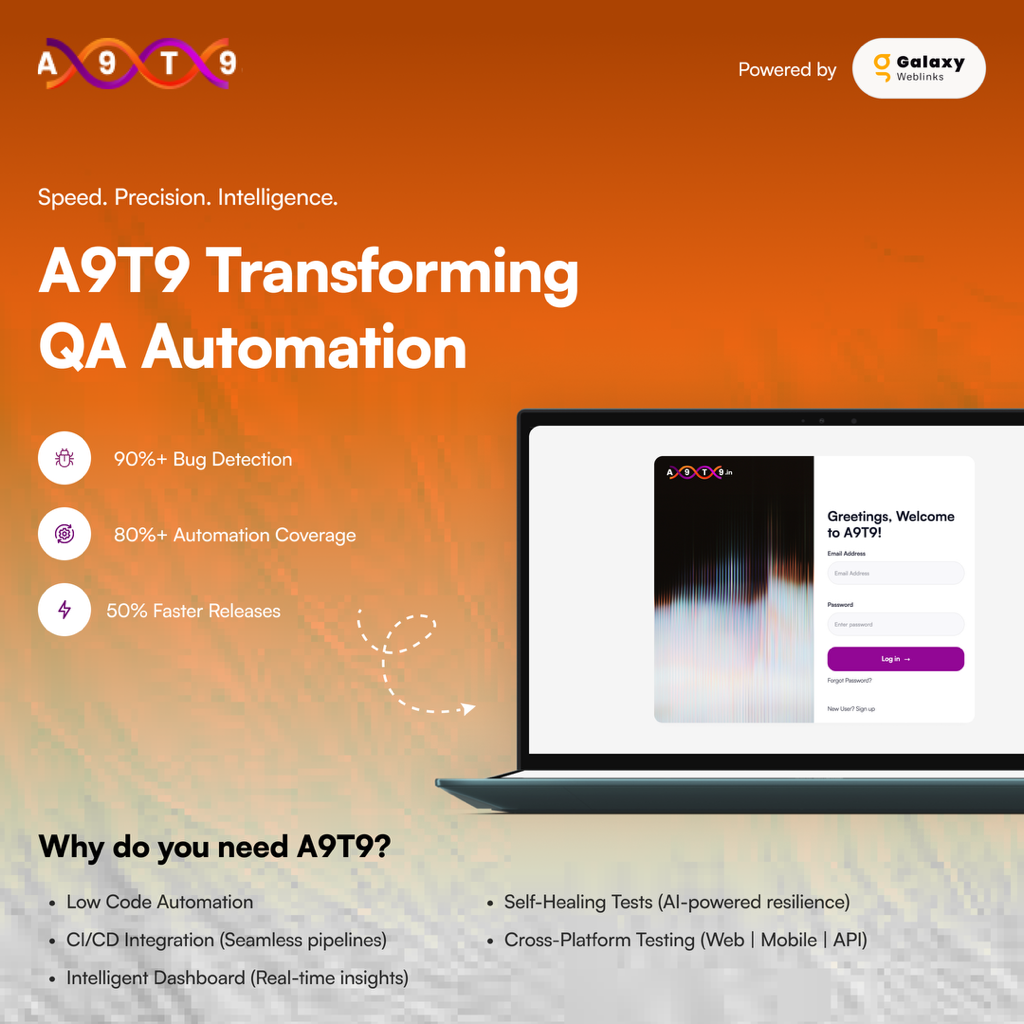
Over the past decade of automation, we have done integration with all contemporary softwares and platforms. We are continuously keeping tab on all new version releases and do continuous up-gradation.


















































An overview of the process and steps adhered to by us.
- Identify Testing Needs: Clearly outline the specific testing requirements, such as functional, performance, security, or regression testing.
- Set Automation Targets: Determine the areas of testing that can be effectively automated and the expected benefits.
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define measurable metrics to track the success of the automation framework, such as test coverage, defect detection rate, and time-to-market.
- Open-Source vs. Proprietary: Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of open-source and proprietary tools based on project requirements, budget, and team expertise.
- Framework Selection: Consider popular frameworks like Selenium WebDriver, Appium, JUnit, TestNG, or Cypress, taking into account language preferences, compatibility, and community support.
- Test Data Management: Implement tools for generating, managing, and masking test data to ensure comprehensive testing.
- Test Case Creation: Develop well-defined test cases covering various scenarios, including positive, negative, and boundary value testing.
- Test Suite Organization: Group related test cases into logical suites for efficient execution and maintenance.
- Prioritization: Assign priorities to test cases based on risk and criticality to optimize testing efforts.
- Coding Standards: Adhere to coding standards and best practices to ensure maintainability and readability.
- Object Identification: Use robust object identification techniques (e.g., XPath, CSS selectors, ID) to locate elements on the application’s interface.
- Data-Driven Testing: Implement data-driven testing to execute the same test case with different data sets.
- Keyword-Driven Testing: Consider keyword-driven testing for a more abstract and maintainable approach.
- Infrastructure: Provision the necessary hardware and software resources to create a stable and reliable test environment.
- Configuration: Configure the test environment to match production settings as closely as possible.
- Virtualization: Utilize virtualization technologies to create isolated test environments for efficient testing.
- Test Execution: Run automated test suites regularly and monitor their execution status.
- Reporting: Generate detailed test reports to track progress, identify defects, and analyze test results.
- Defect Management: Integrate with defect tracking tools to report and manage identified issues.
- Regular Updates: Keep the framework updated with the latest tool versions and best practices.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and refine the framework based on feedback and evolving project needs.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation to guide team members and future users.